Test Android apk file with Robotium
To test an Android apk file using Robotium, it requires to
- Install apk file on device we will use AndroidCalculator apk file, click here to find apk
- Create Test Project using eclipse to test that apk
Note: If android working environment is not set on your machine, follow Set up Android Working Environment
1. Install AUT (Application Under Test) APK
Apk file can be installed on device or emulator. Before installing it needs to make sure that apk file is signed in debug mode. If not it can be signed as debug mode in next steps.
If apk file already has debug mode signatures skip next steps and jump to Load Emulator section.
Note: if you are not sure about the current signed mode of apk file, it’s better to resign it.
Sign Apk file in debug mode
The apk file must have the same certificate signature that your test project has. The signature will identify the author of the android application. Signature means it contains the information like First Name and Last Name of the developer, Name of the Organizational Unit, Organization, City, State, two-letter Country Code. We will un-sign already signed apk file and then again sign it with debug key. Standard tools like Keytool and Jarsigner are used to generate keys and sign applications. For more help visit: http://developer.android.com/guide/publishing/app-signing.html
Important Steps:
1.If you know the certificate signature then use the same signature in test project
2. If you do not know the certificate signature then delete the certificate signature and use the same android debug key signature in both the application and the test project
3. If the application is unsigned then sign the application apk with the android debug key
To un-signed a signed application download java program from http://www.troido.de/re-sign.jar double click on it to open it and drop apk file on it
Or
* Un-zip the apk file
* Delete the META-¬INF folder
* Re‐zip the apk file
* In Dos prompt/Terminal write following commands
> jarsigner -keystore ~/.android/debug.keystore -storepass android -keypass android applicationName.apk androiddebugkey
> zipalign 4 applicationName.apk TempApplicationName.apk
Then rename TempApplicationName.apk to applicationName.apk if you need.
Load Emulator
Load command prompt (windows user) or Terminal (Linux users) and write following command to run emulator
emulator -avd
here the Device Name is our AVD (Android Virtual Device) created in Set up Android Working Environment, it will load emulator in few seconds.
If it shows some error most probably the Android SDK path in not set in PATH environment variable. One can set up Android SDK path in next step, skip next step if emulator is working
Set Up Android SDK Path
Follow the section suits your OS (Operating System) to set SDK path
Linux (ubuntu)
Load terminal and write
echo $PATH
(it will print value of PATH, if Android SDK path is not visible move on next step to add path). To set path enter following command
sudo gedit /etc/bash.bashrc (it will ask password, enter the password)
It will load bash.bashrc file into gedit (text editor) and at end of file add following lines into file and save it.
Note: it is showing the path for all tools necessary for android, based on my current system directory; you need to replace with your own path where Android SDK resides
export PATH=${PATH}:/home/naveed/android-sdk/
export PATH=${PATH}:/home/naveed/android-sdk/tools/
export PATH=${PATH}:/home/naveed/android-sdk/platform-tools/
now reload the Terminal and run emulator -avd command again it will load emulator
Windows
Load Command Prompt and write
echo %PATH%
(it will print value of PATH, if Android SDK path is not visible move on next step to set path). To set path enter following commands one by one
set PATH=${PATH}:c:/naveed/android-sdk/
set PATH=${PATH}:c:/naveed/android-sdk/tools
set PATH=${PATH}:c:/naveed/android-sdk/platform-tools/
Note: it is showing the path for all tools necessary for android, based on my current system directory, you need to replace with your own path where Android SDK resides
Now reload the Command Prompt and run
emulator -avd now it will load emulator
Install AUT apk on Emulator
After the emulator is working, we can now install AUT (application under Test) apk on emulator. To install apk load another instance of command prompt/terminal (based on your os), and write following command to install AndroidCalculator apk on emulator
adb install /AndroidCalculator.apk
the showing the directory where AndroidCalculator.apk is located, in my case it was
adb install /home/naveed/AndroidCalculator.apk
as apk is at my home directory ( I am using ubuntu). You need to enter your own path where apk resides. It will successfully install apk file and show success
Note: For sake of understanding Test Project app will be installed on emulator which will then call/load the AUT (already installed) and perform test scenarios on it. When we will run our Test project through Eclipse it will automatically install it on emulator (will do it in coming sections)
2. Create Test Project
From New window, Drag down to Android option, expand it, and select Android Test Project and Click on Next
On next window under ‘Select TestTarget’ section select ‘This project’ option & click ‘Next’
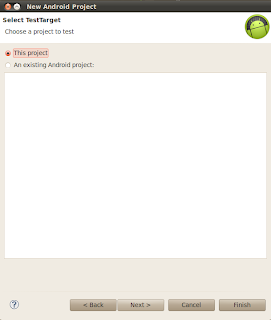
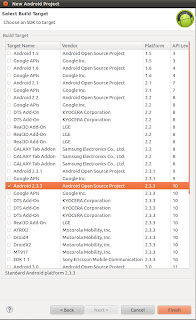 Eclipse will create TestProject with no package,
Eclipse will create TestProject with no package, 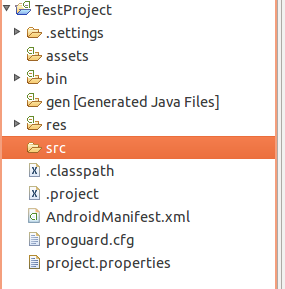
To manually create package right click on project select New > Package. On ‘New Java Package’ window fill package name against ‘Name:’. Like to test AndroidCalculator which has com.calculator package name, TestProject should be com.testcalculator or com.calculator.test package name
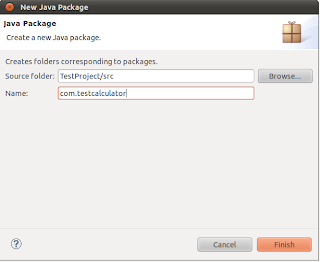
3. Create Test Class
Right click on com.testcalculator package, from New click on Class to add class. Enter class name TestApk (one can put and any name suits) and click on Finish
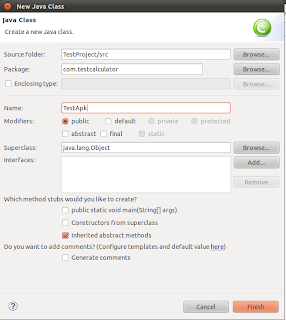
4. Code Test Class
Enter following code into new created TestApk class and save it
package com.testcalculator;
import com.jayway.android.robotium.solo.Solo;
import android.test.ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2;
@SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
public class TestApk extends ActivityInstrumentationTestCase2{
private static final String TARGET_PACKAGE_ID=”com.calculator”;
private static final String LAUNCHER_ACTIVITY_FULL_CLASSNAME=”com.calculator.Main”;
private static Class launcherActivityClass;
static{
try
{
launcherActivityClass=Class.forName(LAUNCHER_ACTIVITY_FULL_CLASSNAME);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public TestApk()throws ClassNotFoundException{
super(TARGET_PACKAGE_ID,launcherActivityClass);
}
private Solo solo;
@Override
protected void setUp() throws Exception
{
solo = new Solo(getInstrumentation(),getActivity());
}
public void testDisplayBlackBox() {
//Enter any integer/decimal value for first editfield, we are writing 10
solo.enterText(0, “10”);
//Enter any interger/decimal value for first editfield, we are writing 20
solo.enterText(1, “20”);
//Click on Multiply button
solo.clickOnButton(“Multiply”);
//Verify that resultant of 10 x 20
assertTrue(solo.searchText(“200”));
}
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
solo.finishOpenedActivities();
}
5. Add Robotium jar
Right click on project (AndroidCalculatorTestApk) select Build Path, and then click on Configure Build Path option. On Properties window click on Libraries tab and add Robotium jar into project
Download Robotium jar from http://code.google.com/p/robotium/downloads/list
6. Targeting AndroidManifest.xml to apk
From project explorer window open AndroidManifest.xml file 
Put ‘com.calculator’ as value of following parameter like above
< span=””>“com.calculator”
7. Run your test
Its time to run test, now right click on AndroidCalculatorTestApk project and Run As AndroidJUnit Test. Wait for some time, it will automatically load AndroidCalculator.apk (installed on emulator) and
* Enter the first & second values into editfields
* Click on Multiply button
* Verify their multiply value
After complete verification it will show the report like below
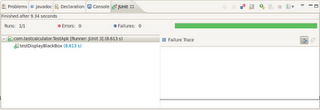
Test can also be run using command prompt/terminal by following simple steps
* Write following command to install AndroidCalculator apk on emulator
> adb install
* Write following command to install AndroidCalculatorTest apk on emulator
> adb install
* Run the test cases:
> adb shell am instrument ‐w com.testcalculator/android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner
Note: Click here to download TestProject project source code