When working with Robotium one may encounter issues that are due to the SDK, Eclipse or how Robotium works.
The intent of this tutorial is to explain and show solutions to common issues that new users experience.
1. NullPointerException when creating a test project for the first time
This problem comes especially with novice, when they for the first time create a new workspace and start working with Robotium.
If we create a new workspace for this tutorial, when creating the Test Project, Eclipse will show error ‘java.lang.NullPointerException’, because it is a new workspace and eclipse is not able to get selected Android resources for first test project.
We can solve this issue by following any of the suggestions below:
1. Create another TestProject & eclipse will automatically get selected resources(for the new one) & not show error for second created Test Project(we can use the second one for our work)
2. First create an Android Project (we can also use Android Sample application bundled with Android SDK), run it, then create Test Project will not show error
2.Java.lan.NoClassDefFoundError: com.jayway.android.robotium.solo.solo
In the latest Android SDK versions (17 or above) java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError:
com.jayway.android.robotium.solo.Solo error is shown if the Robotium jar is not exported. To fix the issue, after adding the Robotium jar go to the “Order & Export” tab and click the check-box besides the Robotium Jar and then click “OK”. Please see the screenshots below.
3. Robotium does not work with all the activities
Important to know that Robotium runs in the same process as the application under test. Due to this Robotium only works with the activities and views within the defined package (see below).
In the AndroidManifest.xml we use the following code to describe which application to test:
android:targetPackage=”com.app.testingapp”
android:name=”android.test.InstrumentationTestRunner” />
“com.app.testingapp” is the package name of the application under test. Robotium is locked to this package.
4. Unstable test case
Robotium contains the following wait methods:
waitForActivity(String name)
Waits for the given Activity.
waitForActivity(String name, int timeout)
Waits for the given Activity.
waitForDialogToClose(long timeout)
Waits for a Dialog to close.
waitForFragmentById(int id)
Waits for a Fragment with a given id to appear.
waitForFragmentById(int id, int timeout)
Waits for a Fragment with a given id to appear.
waitForFragmentByTag(String tag)
Waits for a Fragment with a given tag to appear.
waitForFragmentByTag(String tag, int timeout)
Waits for a Fragment with a given tag to appear.
waitForLogMessage(String logMessage)
Waits for a log message to appear.
waitForLogMessage(String logMessage, int timeout)
Waits for a log message to appear.
waitForText(String text)
Waits for a text to be shown.
waitForText(String text, int minimumNumberOfMatches, long timeout)
Waits for a text to be shown.
waitForText(String text, int minimumNumberOfMatches, long timeout, boolean scroll)
Waits for a text to be shown.
waitForText(String text, int minimumNumberOfMatches, long timeout, boolean scroll, boolean onlyVisible)
Waits for a text to be shown.
waitForView(Class
Waits for a View of a certain class to be shown.
waitForView(Class
Waits for a View of a certain class to be shown.
waitForView(Class
Waits for a View of a certain class to be shown.
waitForView(android.view.View view)
Waits for a given View to be shown.
waitForView(android.view.View view, int timeout, boolean scroll)
Waits for a given View to be shown.
5. Hanging/Freezing test cases
@AfterClass
public void tearDown() throws Exception
{
solo.finishOpenedActivities();
}
6. Problems when resigning APK
Manually re-sign APK
To manually re-sing APK:s follow the below steps:
* Un-zip the APK file
* Delete the META-¬INF folder
* Re‐zip the APK file
It will zip file as “applicationName.apk.zip” , rename it to: “applicationName.apk”
* In Dos prompt/Terminal write following commands> jarsigner -keystore ~/.android/debug.keystore -storepass android -keypass android applicationName.apk androiddebugkey
> zipalign 4 applicationName.apk TempApplicationName.apkThen rename TempApplicationName.apk to applicationName.apk if you want.
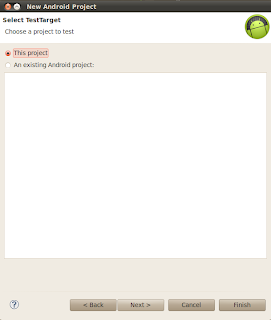
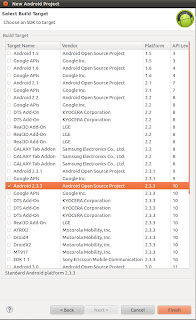 Eclipse will create TestProject with no package,
Eclipse will create TestProject with no package,